研究|婴儿睡眠,有说侧着睡,有说躺着睡,都是医生说的,该听谁的?( 三 )
文章图片
4
摆脱固定思维 , 加强自己的科学的育儿观
很多医生在用自己闲暇时间科普 , 其实也是希望借助信息时代的便利 , 希望将所学 , 所知传播给更多的人 。 我们从来没有像现在一样 , 这么轻易获得如此多的信息 。 在这个信息爆炸的时代 , 给我们提供了太多的便利 。 同样也会带来很多不一样的观点 , 而我们为了适应这个时代 , 必须对于纷繁复杂的信息中 , 有一个科学遴选信息的方法 , 来加强自己的认知 。
无论医生也好 , 宝爸宝妈也罢 , 都需要不断的更新自己的观念 , 医学也是在不断的更新中 , 而抱着一些执念 , 而毫无理由的排斥科学的观念的 , 不是误了自己 , 就是误了他人 。

文章图片
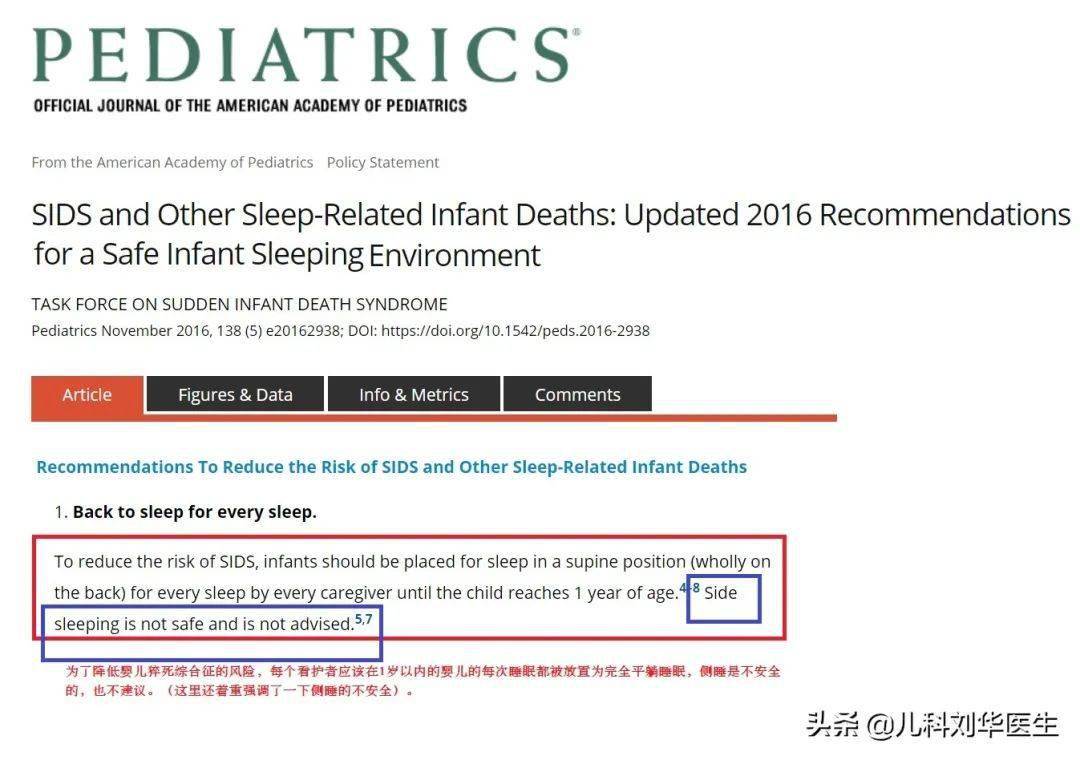
既往关于睡眠安全文章: 严重警告:婴儿睡眠谨防“婴儿猝死综合征”
参考文献
1. Hoffman HJ, Damus K, Hillman L, Krongrad E. Risk factors for SIDS. Results of the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development SIDS Cooperative Epidemiological Study. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1988; 533:13.
2. Willinger M, Hoffman HJ, Hartford RB. Infant sleep position and risk for sudden infant death syndrome: report of meeting held January 13 and 14, 1994, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD. Pediatrics 1994; 93:814.
3. Fleming PJ, Blair PS, Bacon C, et al. Environment of infants during sleep and risk of the sudden infant death syndrome: results of 1993–5 case-control study for confidential inquiry into stillbirths and deaths in infancy. Confidential Enquiry into Stillbirths and Deaths Regional Coordinators and Researchers. BMJ.1996;313 :191– 195
4. Willinger M, Hoffman HJ, Wu KT, et al. Factors associated with the transition to nonprone sleep positions of infants in the United States: the National Infant Sleep Position Study. JAMA.1998;280 :329– 335
5. The Changing Concept of Sudden Infant Death Syndrome: Diagnostic Coding Shifts, Controversies Regarding the Sleeping Environment, and New Variables to Consider in Reducing Risk. Pediatrics, November 2005, 116 (5) 1245-1255;
6. Interactions of infectious symptoms and modifiable risk factors in sudden infant death syndrome. The Nordic Epidemiological SIDS study. Acta Paediatr.1999 May ;88(5) :521-7.
7. Li DK, Petitti DB, Willinger M, et al. Infant sleeping position and the risk of sudden infant death syndrome in California, 1997–2000. Am J Epidemiol.2003;157 :446– 455
- 澎湃新闻|上师大非洲研究中心主任张忠祥:非洲是正在崛起的大陆
- 新药|乙肝在研新药ABI-H0731,II期211研究,安全性数据
- 研究|为何吃饭增加胆固醇合成?武汉大学宋保亮等Nature解密
- 称多|肌痛和乏力,不一定是他汀不良反应!英研究称多为心理反应
- 澎湃新闻|中国十余年研究:玉米生物量增加对产量贡献率为73.71%
- 模拟系统|瑞金新技术(六)| 体外胚胎移植模拟系统提高试管婴儿成功率
- 研究|同感染新冠病毒,为何有人病重死亡,有人甚至不用住院?
- 考核|【妇产要闻】2020年首都医科大学妇产科学硕士研究生临床能力考核在我院顺利完成
- 研究生|本溪市中心医院喜获市唯一一家“中国医科大学研究生培养工作站”称号
- 绅士老司机|32岁舒畅被曝隐婚生子 房中疑有婴儿床和玩具
