爱可可AI论文推介(10月15日)
LG - 机器学习 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 IR - 信息检索
1、[LG]Characterising Bias in Compressed Models
S Hooker, N Moorosi, G Clark, S Bengio, E Denton
[Google Research]
模型压缩放大了深度网络的偏差 。 深度网络通过裁剪、量化等技术实现了高水平压缩 , 总体误差基本没有变化 , 但有一组数据承担了不成比例的高误差部分 , 称为子集压缩识别样本(CIE) , 对于CIE部分 , 压缩放大了算法偏差 , 对未充分表示的特征进行不成比例的修剪会影响性能 , 与通常公平性意义上的考虑相一致 。 CIE集合可通过标注点来进行隔离 。
The popularity and widespread use of pruning and quantization is driven by the severe resource constraints of deploying deep neural networks to environments with strict latency, memory and energy requirements. These techniques achieve high levels of compression with negligible impact on top-line metrics (top-1 and top-5 accuracy). However, overall accuracy hides disproportionately high errors on a small subset of examples; we call this subset Compression Identified Exemplars (CIE). We further establish that for CIE examples, compression amplifies existing algorithmic bias. Pruning disproportionately impacts performance on underrepresented features, which often coincides with considerations of fairness. Given that CIE is a relatively small subset but a great contributor of error in the model, we propose its use as a human-in-the-loop auditing tool to surface a tractable subset of the dataset for further inspection or annotation by a domain expert. We provide qualitative and quantitative support that CIE surfaces the most challenging examples in the data distribution for human-in-the-loop auditing.
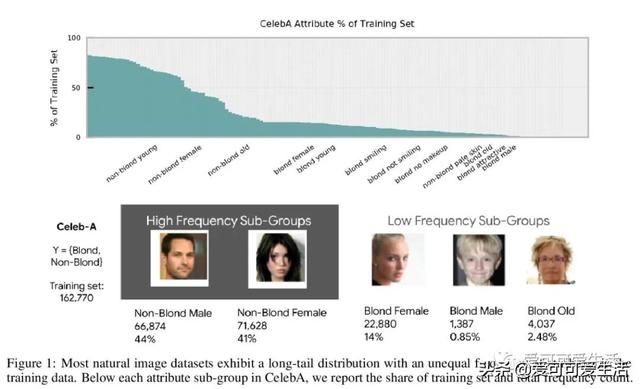 文章插图
文章插图
 文章插图
文章插图
2、[CL] Tired of Topic Models? Clusters of Pretrained Word Embeddings Make for Fast and Good Topics too!
S Sia, A Dalmia, S J. Mielke
[Johns Hopkins University]
预训练词嵌入聚类主题分析 , 对预训练的词嵌入进行聚类 , 同时合并文档信息进行加权聚类 , 并重排头部单词 , 实现无监督文本主题分析 。 实验表明 , 预训练的词嵌入(上下文化或非上下文化) , 与TF加权K-Means和基于TF的重排相结合 , 以较低复杂度和较低的运行时间 , 为传统主题建模提供了一种可行的替代方案 。
Topic models are a useful analysis tool to uncover the underlying themes within document collections. The dominant approach is to use probabilistic topic models that posit a generative story, but in this paper we propose an alternative way to obtain topics: clustering pre-trained word embeddings while incorporating document information for weighted clustering and reranking top words. We provide benchmarks for the combination of different word embeddings and clustering algorithms, and analyse their performance under dimensionality reduction with PCA. The best performing combination for our approach performs as well as classical topic models, but with lower runtime and computational complexity.
 文章插图
文章插图
- 谷歌:想发AI论文?请保证写的是正能量
- 谷歌对内部论文进行“敏感问题”审查!讲坏话的不许发
- 2019年度中国高质量国际科技论文数排名世界第二
- 谷歌通过启动敏感话题审查来加强对旗下科学家论文的控制
- Arxiv网络科学论文摘要11篇(2020-10-12)
- 聚焦城市治理新方向,5G+智慧城市推介会在长举行
- 中国移动5G新型智慧城市全国推介会在长沙举行
- 年年都考的数字鸿沟有了新进展?彭波老师的论文给出了解答!
- 打开深度学习黑箱,牛津大学博士小姐姐分享134页毕业论文
- 爱可可AI论文推介(10月9日)
