快速介绍Python数据分析库pandas的基础知识和代码示例
 文章插图
文章插图
"软件工程师阅读教科书作为参考时不会记住所有的东西 , 但是要知道如何快速查找重要的知识点 。 "
为了能够快速查找和使用功能 , 使我们在进行机器学习模型时能够达到一定流程化 。 我创建了这个pandas函数的备忘单 。 这不是一个全面的列表 , 但包含了我在构建机器学习模型中最常用的函数 。 让我们开始吧!
本附注的结构:
· 导入数据
· 导出数据
· 创建测试对象
【快速介绍Python数据分析库pandas的基础知识和代码示例】· 查看/检查数据
· 选择查询
· 数据清理
· 筛选、排序和分组
· 统计数据
首先 , 我们需要导入pandas开始:
import pandas as pd导入数据使用函数pd.read_csv直接将CSV转换为数据格式 。
注意:还有另一个类似的函数pd 。 read_excel用于excel文件 。
# Load data df = pd.read_csv('filename.csv') # From a CSV filedf = pd.read_excel('filename.xlsx') # From an Excel file导出数据tocsv()将数据存储到本地的文件 。 我们可以通过df[:10].tocsv()保存前10行 。 我们还可以使用df.to_excel()保存和写入一个DataFrame到Excel文件或Excel文件中的一个特定表格 。
df.to_csv('filename.csv') # Write to a CSV filedf.to_excel('filename.xlsx') # Write to an Excel file创建测试对象从输入的数据建立一个DataFrame
# Build data frame from inputted datadf = pd.DataFrame(data = http://kandian.youth.cn/index/{'Name': ['Bob', 'Sally', 'Scott', 'Katie'], 'Physics': [68, 74, 77, 78], 'Chemistry': [84, 100, 73, 90], 'Algebra': [78, 88, 82, 87]})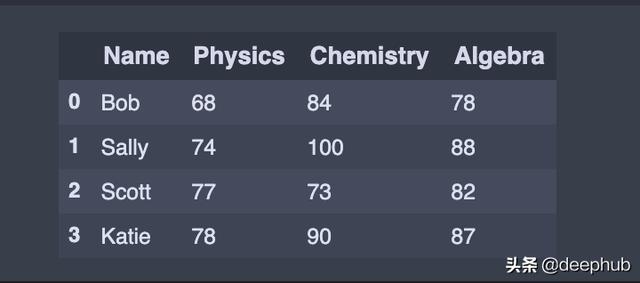 文章插图
文章插图
或者从列表中创建一个series
#Create a series from an iterable my_listmy_list = [['Bob',78],['Sally',91],['Scott',62],['Katie',78],['John',100]]df1 = pd.Series(my_list) # Create a series from an iterable my_list 文章插图
文章插图
查看/检查数据head():显示DataFrame中的前n条记录 。 我经常把一个数据档案的最上面的记录打印在我的jupyter notebook上 , 这样当我忘记里面的内容时 , 我可以回头查阅 。
df.head(3) # First 3 rows of the DataFrame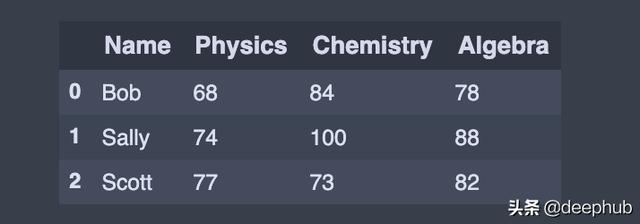 文章插图
文章插图
tail():返回最后n行 。 这对于快速验证数据非常有用 , 特别是在排序或附加行之后 。
df.tail(3) # Last 3 rows of the DataFrame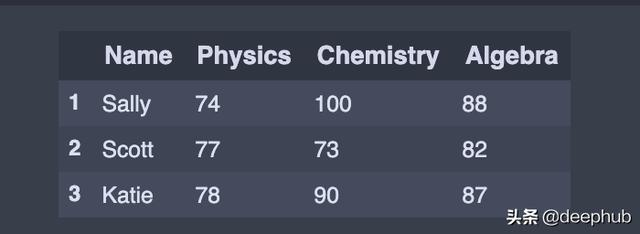 文章插图
文章插图
添加或插入行要向DataFrame追加或添加一行 , 我们将新行创建为Series并使用append()方法 。
在本例中 , 将新行初始化为python字典 , 并使用append()方法将该行追加到DataFrame 。
在向append()添加python字典类型时 , 请确保传递ignore_index=True , 以便索引值不会被使用 。 生成的轴将被标记为编号series0,1 , … ,n-1 , 当连接的数据使用自动索引信息时 , 这很有用 。
append() 方法的作用是:返回包含新添加行的DataFrame 。
#Append row to the dataframe, missing data (np.nan)new_row = {'Name':'Max', 'Physics':67, 'Chemistry':92, 'Algebra':np.nan}df = df.append(new_row, ignore_index=True)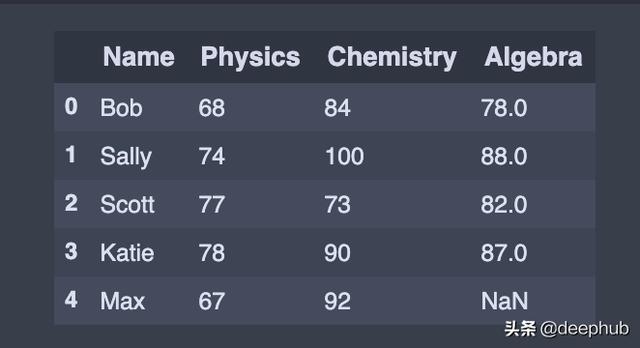 文章插图
文章插图
向DataFrame添加多行
# List of serieslist_of_series = [pd.Series(['Liz', 83, 77, np.nan], index=df.columns),pd.Series(['Sam', np.nan, 94,70], index=df.columns ),pd.Series(['Mike', 79,87,90], index=df.columns),pd.Series(['Scott', np.nan,87,np.nan], index=df.columns),]# Pass a list of series to the append() to add multiple rowsdf = df.append(list_of_series , ignore_index=True)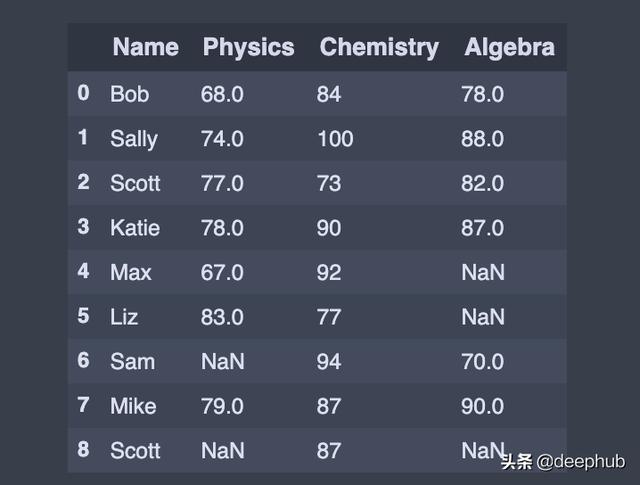 文章插图
文章插图
我们也可以添加新的列
# Adding a new column to existing DataFrame in Pandassex = ['Male','Female','Male','Female','Male','Female','Female','Male','Male']df['Sex'] = sex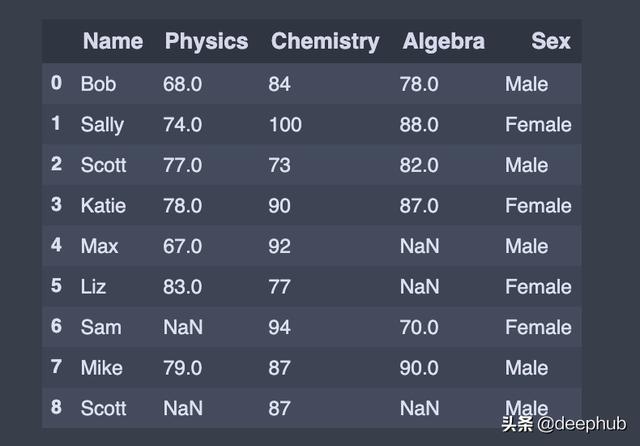 文章插图
文章插图
info()函数用于按列获取标题、值的数量和数据类型等一般信息 。 一个类似但不太有用的函数是df.dtypes只给出列数据类型 。
df.info() #Index, Datatype and Memory information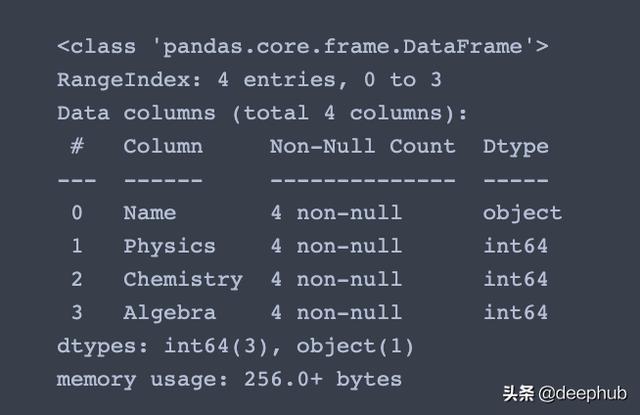 文章插图
文章插图
# Check data type in pandas dataframedf['Chemistry'].dtypes >>> dtype('int64')#Convert Integers to Floats in Pandas DataFramedf['Chemistry'] = df['Chemistry'].astype(float) df['Chemistry'].dtypes>>> dtype('float64')# Number of rows and columnsdf.shape >>> (9, 5)
- GB|备货充足要多少有多少,5000mAh+128GB,红米新机首销快速现货
- 页面|如何简单、快速制作流程图?上班族的画图技巧get
- 介绍|5分钟介绍各种类型的人工智能技术
- 能力|美国研发快速法评估神经网络的不确定性 改进自动驾驶车决策能力
- 入门|做抖音影视赚钱比工资多,教大家新手也可快速入门
- 平台好友|《妄想山海》好友列表介绍
- 告诉|阿里大佬告诉你如何一分钟利用Python在家告别会员看电影
- Python源码阅读-基础1
- Python调用时使用*和**
- 程序员学英语第1天——JavaScript 程序测试的介绍1
