Java8:2万字20个实例玩转集合—筛选、归约、分组、聚合( 四 )
工资之和:49300,49300,49300最高工资:9500,9500
3.6 收集(collect)collect , 收集 , 可以说是内容最繁多、功能最丰富的部分了 。 从字面上去理解 , 就是把一个流收集起来 , 最终可以是收集成一个值也可以收集成一个新的集合 。
collect主要依赖java.util.stream.Collectors类内置的静态方法 。
3.6.1 归集(toList/toSet/toMap)因为流不存储数据 , 那么在流中的数据完成处理后 , 需要将流中的数据重新归集到新的集合里 。 toList、toSet和toMap比较常用 , 另外还有toCollection、toConcurrentMap等复杂一些的用法 。
下面用一个案例演示toList、toSet和toMap:
public class StreamTest { public static void main(String[] args) {List运行结果:
toList:[6, 4, 6, 6, 20]toSet:[4, 20, 6]toMap:{Tom=mutest.Person@5fd0d5ae, Anni=mutest.Person@2d98a335}
3.6.2 统计(count/averaging)Collectors提供了一系列用于数据统计的静态方法:
案例:统计员工人数、平均工资、工资总额、最高工资 。
public class StreamTest { public static void main(String[] args) {List personList = new ArrayList();personList.add(new Person("Tom", 8900, 23, "male", "New York"));personList.add(new Person("Jack", 7000, 25, "male", "Washington"));personList.add(new Person("Lily", 7800, 21, "female", "Washington"));// 求总数Long count = personList.stream().collect(Collectors.counting());// 求平均工资Double average = personList.stream().collect(Collectors.averagingDouble(Person::getSalary));// 求最高工资Optional运行结果:
员工总数:3员工平均工资:7900.0员工工资总和:23700员工工资所有统计:DoubleSummaryStatistics{count=3, sum=23700.000000,min=7000.000000, average=7900.000000, max=8900.000000}
3.6.3 分组(partitioningBy/groupingBy)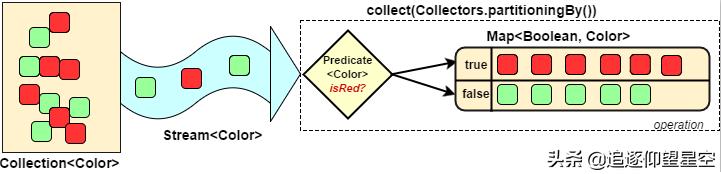 文章插图
文章插图
案例:将员工按薪资是否高于8000分为两部分;将员工按性别和地区分组
public class StreamTest { public static void main(String[] args) {List personList = new ArrayList();personList.add(new Person("Tom", 8900, "male", "New York"));personList.add(new Person("Jack", 7000, "male", "Washington"));personList.add(new Person("Lily", 7800, "female", "Washington"));personList.add(new Person("Anni", 8200, "female", "New York"));personList.add(new Person("Owen", 9500, "male", "New York"));personList.add(new Person("Alisa", 7900, "female", "New York"));// 将员工按薪资是否高于8000分组Map> part = personList.stream().collect(Collectors.partitioningBy(x -> x.getSalary() > 8000));// 将员工按性别分组Map> group = personList.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Person::getSex));// 将员工先按性别分组 , 再按地区分组Map>> group2 = personList.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Person::getSex, Collectors.groupingBy(Person::getArea)));System.out.println("员工按薪资是否大于8000分组情况:" + part);System.out.println("员工按性别分组情况:" + group);System.out.println("员工按性别、地区:" + group2); }}
- 加急|古代8百里加急究竟有多快?需要骑马20个小时,速度媲美顺丰快递!
- 建成|“听”书全覆盖,大连建成20个“残疾人有声图书馆”
- Harvest被攻击,20个ETH套利2400万美元,CRV却涨了
- 品牌|品牌能够采用的20个推特创意技巧
- 未来|创“芯”未来!20个高新技术产业项目落子德清天安云谷
- 项目|创“芯”未来!20个高新技术产业项目落子德清天安云谷
- 京东华硕RTX3080被指耍猴,数十万人预定,只有20个评论
- Java8新特性探索之函数式接口
- 5G+工业互联网发展报告:20个省市政策支持,应用是重点
- 黑马|一年销量两个亿!他仅花了20个月,做成拼多多上最大的行业黑马
