提出了一|【泡泡一分钟】基于三维子图显著性的主动SLAM在水下体积探测中的应用( 二 )
表1 五次运行的平均云间错误。从左到右,最终映射误差减小,闭环数增加。
文章插图
图11 (a) 地面真实点云与我们的合成图,其中热图显示云间的误差。(b) 对于相同的运行,我们绘制最终占用网格地图的横截面(红色:已占用,白色:空闲空间)。(c) 好的和坏的闭环候选者覆盖在全局映射内。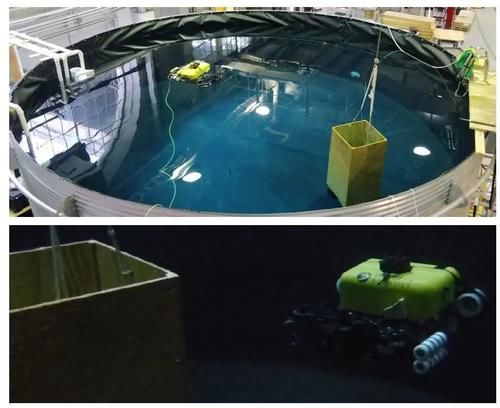
文章插图
图12 现实世界的坦克环境和HAUV运行我们的方法。
表2 三次运行中的平均云间错误。我们的方法提供了更好的地图质量,但是闭环的次数较少。这归因于基线方法因漂移产生的不正确/简并的匹配。通常,具有真实数据的闭环质量很差,只会导致地图质量的改善很小。
表3 用于实际实验的系统参数
Abstract
In this paper, we present an active SLAM framework for volumetric exploration of 3D underwater environments with multibeam sonar. Recent work in integrated SLAM and planning performs localization while maintaining volumetric free-space information. However, an absence of informative loop closures can lead to imperfect maps, and therefore unsafe behavior. To solve this, we propose a navigation policy that reduces vehicle pose uncertainty by balancing between volumetric exploration and revisitation. To identify locations to revisit, we build a 3D visual dictionary from real-world sonar data and compute a metric of submap saliency. Revisit actions are chosen based on propagated pose uncertainty and sensor information gain. Loop closures are integrated as constraints in our pose-graph SLAM formulation and these deform the global occupancy grid map. We evaluate our performance in simulation and real-world experiments, and highlight the advantages over an uncertainty-agnostic framework.
- 抖音|抖音如何获取更多流量?一文读懂直播自然流量提升技巧
- 亏损|爱奇艺"水逆"一整年
- 华为鸿蒙系统|鸿蒙是安卓“换皮”产品?一亿多用户,难道还不足以说明问题
- playstation5|手慢就没有了!索尼PS5国行版将在双十二补货:库存一万台
- 基站|华为一手养肥的这家小巨人,真这么值钱吗?
- 小米科技|比双十一的价格还低!小米11pro还值得入手吗?
- oppo reno|到OPPO线下体验了一番,终于知道Reno7系列为什么卖得这么好了
- 索尼Xperia|力压iPhone13 Pro Max,续航排名第一,仅售1699元
- 优派|美国很满意:150多家芯片厂商,都“自愿”提交了详细数据
- |跌至3099元!8GB运存+128GB+骁龙865,唯一缺陷不是新手机
